Detecting DNA from a single cell is vital for the identification of genetic disorders and diseases. Analyzing single DNA molecules has been possible for some time now; however, it is not possible to directly detect samples at the point of extraction without any need for successive steps.
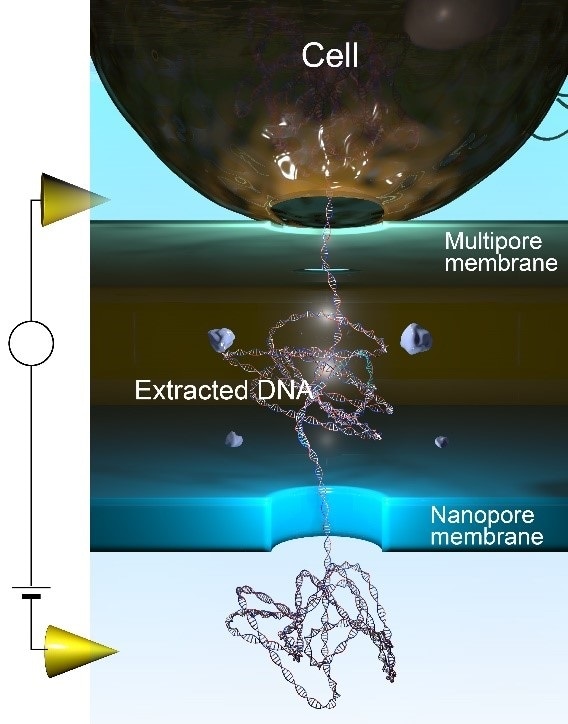
Extractions and detections of single-molecule DNA from a cell using a 3D-integrated nanopore. Image Credit: Makusu Tsutsui et al.
Recently, scientists at SANKEN, Osaka University revealed a process of releasing DNA at the point of measurement. Their results were published in the Small Methods journal.
Nanopores are extremely small holes found in biology or can be purpose engineered. There are interesting signs of progress in employing nanopores as gateways that enable close monitoring as molecules pass through one after the other. For instance, the individual DNA bases passing through a pore have been found to enable whole-genome sequencing.
In spite of these notable steps in single-molecule detection, it is indispensable to increase the concentration of DNA samples for successful measurement as there was no possibility of reliably getting the molecules to the measurement pore.
The scientists developed a 3D-integrated nanopore that can break cells immediately before the measurement. The released molecules can be effectively delivered to the sensing zone and measured without the need to carry out any further steps that might introduce errors.
Our sensor has two important parts. The first is a layer that contains numerous holes that are much smaller than a cell. An electrostatic field is used to rupture the cell and certain released substances can pass through holes while larger debris cannot, essentially providing a filter. Below this filter layer, separated by a spacer, is a single nanopore in a second membrane, where the measurements are made.”
Makusu Tsutsui, Study First Author, Osaka University
While applying a voltage, current flows through the pore due to salt ions in the surrounding solution. This current is partly blocked when large DNA molecules pass through the pore, and the changes offer information regarding the large molecules. For instance, whether the molecule—which could be millimeters in length—is folded.
The filtering effect of our 3D-integrated nanopore prevents blockage of the measurement pore making it robust to use. We, therefore, expect it to be used in new technologies for rapidly detecting mutant viruses at the genome level.”
Tomoji Kawai, Study Corresponding Author, Osaka University
Source:
Journal reference:
Tsutsui, M., et al. (2021) Detecting Single Molecule Deoxyribonucleic Acid in a Cell Using a Three-Dimensionally Integrated Nanopore. Small Methods. doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202100542.