The two rounds of whole-genome duplication that occurred throughout the evolution of vertebrates were followed by functional divergence in terms of regulatory circuits as well as gene expression patterns. Amphioxus is a good model for examining the genesis and evolution of vertebrates since it is a primitive and slowly developing chordate species.
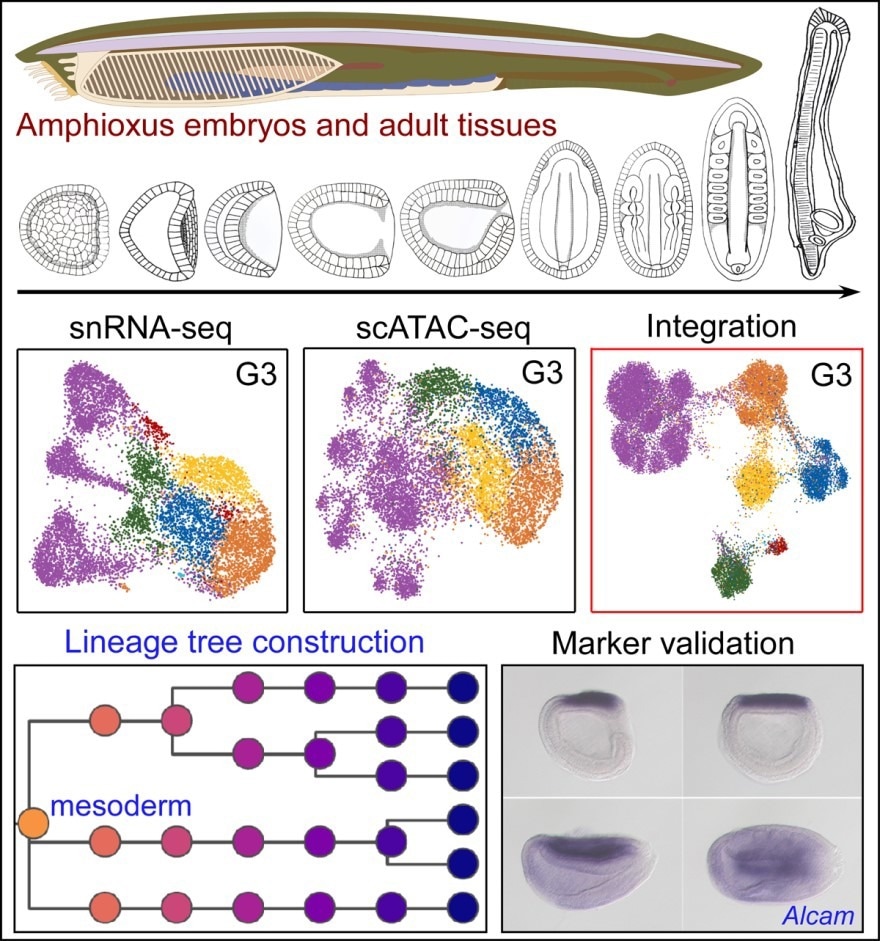 Schematic presentation of the main findings of this research: (1) a snRNA-seq atlas of amphioxus developmental embryos and multiple adult tissues and a scATAC-seq atlas of amphioxus developmental embryos; (2) a developmental tree for amphioxus cell fate commitment and lineage specification; and (3) Computational identification and validation of lineage specific markers. Image Credit: MAO et al.
Schematic presentation of the main findings of this research: (1) a snRNA-seq atlas of amphioxus developmental embryos and multiple adult tissues and a scATAC-seq atlas of amphioxus developmental embryos; (2) a developmental tree for amphioxus cell fate commitment and lineage specification; and (3) Computational identification and validation of lineage specific markers. Image Credit: MAO et al.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Kunming Institute of Zoology’s research team, under the direction of developmental biologist Prof. MAO Bingyu, has published the single-nucleus RNA-seq (snRNA-seq) and single-cell assay for transposase-accessible chromatin (ATAC)-seq (scATAC-seq) atlas for the amphioxus, a cephalochordate and important species for understanding the evolution of vertebrates.
On June 21st, 2022, the results were released in Cell Reports.
In both model and non-model animals, such as humans, mice, zebrafish, frogs, and sea squirts, transcriptional and chromatin-accessibility profiling at the single-cell level is being utilized more often to analyze the early developmental program.
MAO and their colleagues reported the snRNA-seq and scATAC-seq analysis for various stages of the amphioxus Branchiostoma floridae, covering embryogenesis and adult tissues, in order to analyze the mechanisms of cell lineage specification and the logic of the signaling pathways of amphioxus embryos and shed light on the origin of vertebrates.
With the use of these datasets, the researchers constructed the developmental tree for amphioxus cell fate commitment with lineage specification, and by integrated analysis, they identified the fundamental essential regulators.
Furthermore, in amphioxus and other chordate model organisms, the cross-species study also found comparable developmental trajectories, genetic regulatory networks, and regulatory modules.
The data produced for this work are accessible on the AmphioxusAtlas online platform at https://lifeomics.shinyapps.io/shinyappmulti/.
The data could be valuable for understanding the origin and evolution of chordates and throw light upon the genetic and epigenetic mechanism underlying the phenotype novelty of chordates during evolution.”
Prof. Bingyu Mao, Study Co-Corresponding Author and Developmental Biologist, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Source:
Journal reference:
Ma, P., et al. (2022) Joint profiling of gene expression and chromatin accessibility during amphioxus development at single-cell resolution. Cell Reports. doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110979.