Every year, almost eight million tons of plastic wind up in the oceans, posing a major threat to the ecosystem and human health. Biodegradable bioplastics may be a feasible alternative. A research team has published a novel technique for producing protein-based polymers that are easy to manufacture, biodegradable, and biocompatible, as well as having good mechanical qualities.
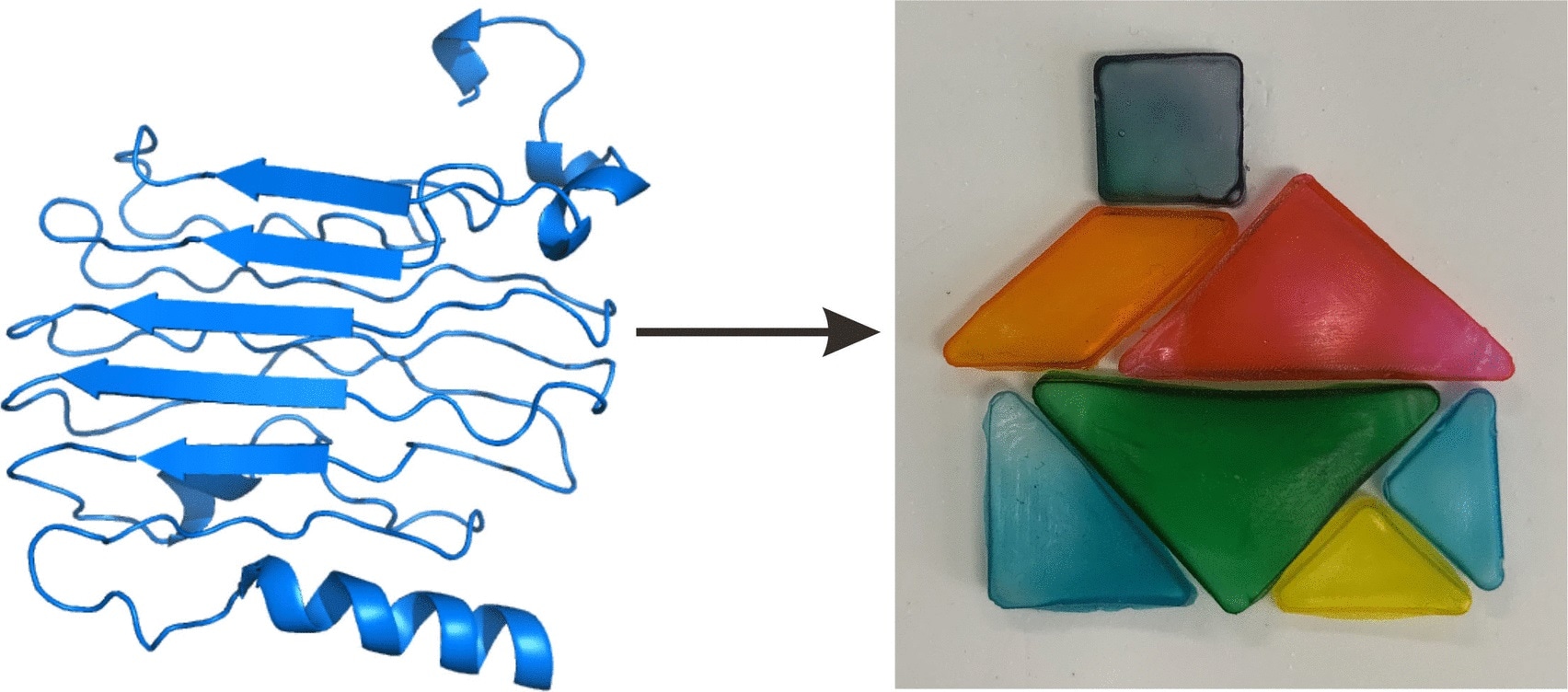
Image Credit: Angewandte Chemie.
The study was published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Plastics based on petrochemicals are prevalent, whether as packaging or toys, mulch films or cars—demand is growing, and so are the mountains of rubbish. In most situations, bioplastics made from natural materials such as starch or synthetic biomaterials such as polylactic acid have shown insufficient durability, biocompatibility, and/or biodegradability.
Additionally, they frequently need complicated, energy-intensive processing procedures as well as harmful chemicals.
New bioplastics with qualities that can be modified according to requirement have been introduced by a team led by Jingjing Li and Yawei Liu (Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, China), as well as Bo Wei (First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital).
Researchers achieved this by developing and producing two lysine-rich proteins in bacterial cultures: “ELP” is a polypeptide that resembles elastin, a connective tissue protein. It lacks distinct folding, resulting in hardness and flexibility. ELP is combined with crystalline segments of a squid protein with a β-sheet structure to form “SRT.”The lysine amino side-groups of ELP (or SRT) crosslink with a polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivative(among other things, PEG is utilized in pharmaceuticals). The material can simply be dried in a mold if the crosslinking happens in water. The end product is bioplastic that is robust, clear, and solvent-resistant. The percentage of PEG may be changed to alter the mechanical characteristics.
This enables the manufacturing of high-mechanical-strength bioplastics in any shape at room temperature, without the need for harmful chemicals or difficult processing procedures like liquefaction, extrusion, or blow molding. They have breaking stress that is higher than that of many commercial polymers. One issue is that they swell when exposed to water.
ELP gels into soft, elastic bioplastics when crosslinked in a water/glycerol solution. Wet spinning was also employed to create biofibers that are as strong as biotechnology spider silks. All of the novel protein-based bioplastics are totally degraded by the natural enzyme elastase.
This new, harmless bioplastic, which can be colored with food coloring, might be used to build toys. Due to its hemostatic properties, this material may also be used to seal wounds. Within a few weeks, the implants had entirely broken down.
ELP might be polymerized using peptides that have been encoded with codes using their particular amino acid sequences to hold information. Sequencing allowed the information to be read back. This would allow for a higher information density than DNA data storage now allows.
Source:
Journal reference:
Su, J., et al. (2022) Biosynthetic Structural Proteins with Super Plasticity, Extraordinary Mechanical Performance, Biodegradability, Biocompatibility, and Information Storage Ability. Angewandte Chemie. doi.org/10.1002/anie.202117538.