Protein degraders, which cause target proteins to break down, are thought to be the “next-generation drugs” because they may eliminate disease-causing proteins from cells. Protein degraders, such as thalidomide and its derivatives (Immunomodulatory drugs/IMiDs), work by binding to cereblon (CRBN)—a component of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (a proteolytic enzyme), to cause the breakdown of certain proteins.
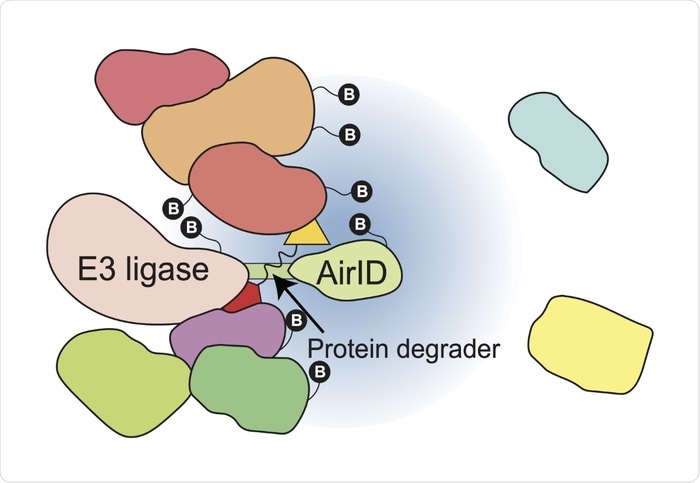
Biotinylation of interacting proteins in a protein degrader-dependent manner. Image Credit: Satoshi Yamanaka, Ehime University.
Molecular glue-type proteolytic inducers are IMiDs that act as a “molecular glue,” causing protein breakdown by attracting target proteins to E3 ubiquitin ligase. Molecular glue-type protein degraders have become interesting compounds for use in addressing numerous diseases as a result of the therapeutic success of IMiDs.
Furthermore, proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are being developed, which are chimeric compounds consisting of an E3 ubiquitin ligase (E3 binder), such as IMiDs, and a molecule that binds to a target protein (target binder). PROTACs are intended to make it possible to target proteins that have previously been difficult to target with therapeutic drugs.
For the development and clinical use of protein degraders, it is critical to examine proteins that interact with E3 ubiquitin ligase and are driven to degrade. AirID (ancestral BirA for proximity-dependent biotin identification) was created by this research group in 2020 as a proximal-dependent biotinylation labeling enzyme suitable for protein-protein interaction study.
As a result, researchers worked to develop a technique for identifying interacting proteins in a protein degrader-dependent way.
Researchers discovered that an AirID-fused E3 ubiquitin ligase, such as AirID-CRBN, may biotinylate the target proteins of protein degraders in cells in the work. Moreover, scientists found that the avidin-like protein tamabidine 2-REV may be used to concentrate biotinylated peptides for mass spectrometric investigation of protein degrader-dependent interactions.
Researchers discovered ZMYM2 (zinc finger MYM-type protein 2) as a target protein of pomalidomide, a thalidomide derivative, using this approach. Pomalidomide also degrades the ZMYM2-FGFR1 fusion protein, which is linked to hematological cancer.
Researchers also confirmed that this method of analysis can be utilized for known protein degraders like Indisulam and PROTACs. These results suggest that fusing AirID with E3 ubiquitin ligase allows for a complete investigation of protein degrader interacting proteins.
This AirID-based analytical approach may be used for a variety of protein degraders that will be developed in the future. Various protein degraders are now being developed for a variety of diseases, with some of them already in clinical trials. However, because of the powerful impacts of protein degraders, it is important to look at how they interact with proteins that are not meant to cause problems.
The findings of this study revealed that E3 ligase interacts with numerous proteins in a protein degrader-dependent way. Based on these findings, it is believed that using this analytical approach will lead to the discovery of protein degrader mechanisms of action and the creation of drugs with fewer adverse effects.
Source:
Journal reference:
Yamanaka, S., et al. (2022) A proximity biotinylation-based approach to identify protein-E3 ligase interactions induced by PROTACs and molecular glues. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27818-z.