Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Mar 3 2023
A new method, DNA End tailing and sequencing (DEtail-seq), for meiotic DNA double-strand break (DSB) profiling was developed recently by Dr Qianwen Sun’s group from Tsinghua University, Dr Wei Li’s group from Guangzhou Medical University, Dr Hui Jiang’s group from Peking University Third Hospital, and Wei Xu’s group from Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
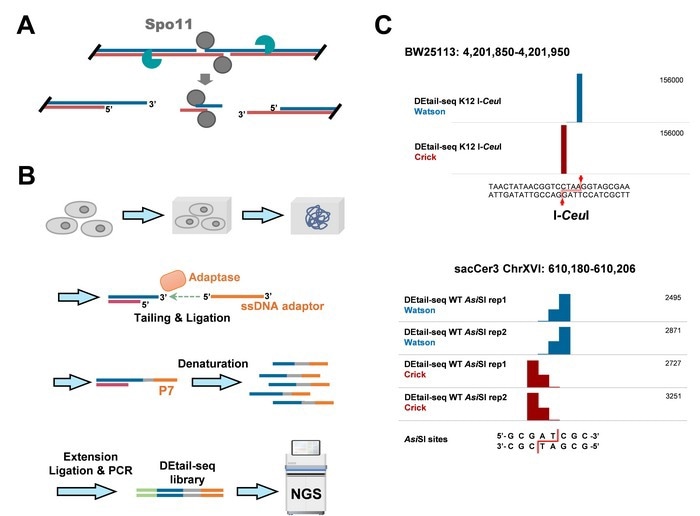 (A) Illustration of meiotic DSB induced by Spo11; (B) Brief schematic of DEtail-seq detection of DSBs with 3’ overhangs; (C) Snapshots showing the DEtail-seq signals at restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Image Credit: ©Science China Press.
(A) Illustration of meiotic DSB induced by Spo11; (B) Brief schematic of DEtail-seq detection of DSBs with 3’ overhangs; (C) Snapshots showing the DEtail-seq signals at restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Image Credit: ©Science China Press.
Meiosis is a basic process required for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Meiotic recombination is started during meiosis by Spo11-induced programmed DSBs and results in the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, which is advantageous for genetic diversity.
As a result, accurate mapping of meiotic DSBs is required to comprehend the mechanism of meiotic homologous recombination. Upstream DNA ends, downstream DNA ends, and Spo11-bound oligos are the three components of Spo11-induced meiotic DSBs. Upstream and downstream DNA ends both have 3' overhang structures with a free 3' ssDNA end.

Image Credit: Novikov Aleksey/Shutterstock.com
The reported earlier methods for meiotic DSB detection have some drawbacks, like low sensitivity, cumbersome operation, and low resolution. To address these issues, the authors developed the DEtail-seq technique, in which the 3' end of the DNA break is directly ligated to the 1st adaptor using Adaptase, an extremely effective single-stranded DNA ligation system, and the final library is crafted in a series of steps.
The position of the 3' end of the DNA break was mapped after sequencing and data analysis. The recognition of restriction endonuclease cleavage sites demonstrated that the DEtail-seq technique had extremely high resolution, approaching single nucleotide resolution.
The researchers profiled meiotic DSBs in budding yeast, mouse, and human germ cells using the DEtail-seq technique and discovered novel meiotic DSB features. The mouse data analysis revealed that the meiotic DSB signal at the leptotene/zygotene stage was enhanced around de novo H3K4me3 peaks at the leptotene stage.
Human data analysis revealed that the meiotic DSB signal was enriched in CTCF+ enhancer regions. The researchers assume that the DEtail-seq technique is an effective tool for studying meiosis in different species.
Source:
Journal reference:
Xu, W., et al. (2023) DEtail-seq is an ultra-efficient and convenient method for meiotic DNA break profiling in multiple organisms. Science China Life Sciences. doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2277-y.