Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Jun 28 2023
In their study performed, the research group discusses their novel view of euchromatin present in the cell and displays how the disclosed organization is appropriate to genome functions.
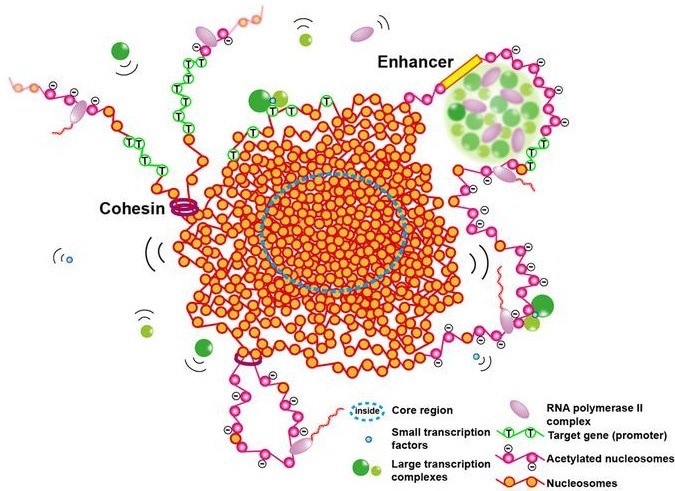 Nucleosomes (orange spheres) in euchromatin form a condensed domain with cohesins (rings). Transcription occurs on the domain surface with various transcription factors and RNA Polymerase II. Image Credit: Sachiko Tamura & Kazuhiro Maeshima, National Institute of Genetics, ROIS. Reproduced from Trends in Cell Biology.
Nucleosomes (orange spheres) in euchromatin form a condensed domain with cohesins (rings). Transcription occurs on the domain surface with various transcription factors and RNA Polymerase II. Image Credit: Sachiko Tamura & Kazuhiro Maeshima, National Institute of Genetics, ROIS. Reproduced from Trends in Cell Biology.
Our ultimate goal is to reveal how genomic information is searched and read out in living cells.”
Kazuhiro Maeshima, Study Leading Author and Professor, National Institute of Genetics and SOKENDAI
Chromatin explains the combination of DNA and proteins in the cells of humans and also other eukaryotes. As per the normal textbook models, chromatin takes place in two forms—heterochromatin, which is more condensed and usually not transcribed, and euchromatin, which is less condensed and could be transcribed.
Transcription is known as the activity where a cell makes an RNA copy of a DNA molecule, a process that is essential for life. The research team concentrated their study on euchromatin.
Image Credit: Design_Cells/Shutterstock.com
The team recommends in their opinion paper that the euchromatin present in higher eukaryotic cells like human cells is not open essentially. Rather, they suggest that euchromatin develops into condensed liquid-like domains, with sizes varying from 100 to 300 nm in diameter.
The advanced imaging studies performed in recent times involving 3D structured illumination microscopy (SIM), focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy, and single molecule imaging revealed local chromatin conformation and have displayed proof that euchromatin forms condensed domains.
Complementary to this, recent genomics methods also disclosed that only restricted genomic regions are always accessible. Such studies indicate that condensed domains have been folded irregularly and dynamically and consist of liquid-like properties.
Compared to the heterochromatic domains, the euchromatic domains are smaller in size, resulting in an increased surface area-to-volume-ration in euchromatin, which could also describe the variation in transcriptional activity.
Open chromatin regions where transcription happens seem to be limited at the domain surfaces or boundaries between domains. Also, condensed domains have dynamic liquid-like properties, which give certain accessibility for the inside, and allow cells to activate transcription and other DNA transactions, such as DNA replication and repair.”
Shiori Iida, Study Co-First Author, Research Organization of Information and Systems
It is not possible to categorize chromatin just simply into heterochromatin and euchromatin by its open or closed form. In opposition to accepted dogma, euchromatin domains are not opened completely but instead condensed.
Condensed chromatin seems to be the default chromatin state in higher eukaryotic cells, possibly functional units in DNA transactions, and assembly units like Lego blocks for the chromosome during cell division.”
Kazuhiro Maeshima, Study Leading Author and Professor, National Institute of Genetics and SOKENDAI
Going forward, the team believes that their work will intensify the knowledge of transcriptional regulation and also other DNA transactions.
“The next step is to investigate how the condensed domains are regulated during cell differentiation or developmental processes to execute specific cellular functions,” stated Masa Shimazoe, one of the co-authors.
The research group includes Kazuhiro Maeshima, Shiori Iida, Masa A. Shimazoe, and Satoru Ide, who work at the National Institutes of Genetics, Shizuoka, Mishima, and the Graduate Institute for Advanced Studies, (SOKENDAI); and Sachiko Tamura, who works at the National Institutes of Genetics, Mishima, Shizuoka.
Source:
Journal reference:
Maeshima, K., et al. (2023) Is euchromatin really open in the cell?. Trends in Cell Biology. doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2023.05.007.