Scientists have called for labeling to warn the public about levels of arsenic in rice after their research found half of the rice varieties studied exceeded maximum limits on the deadly toxin.
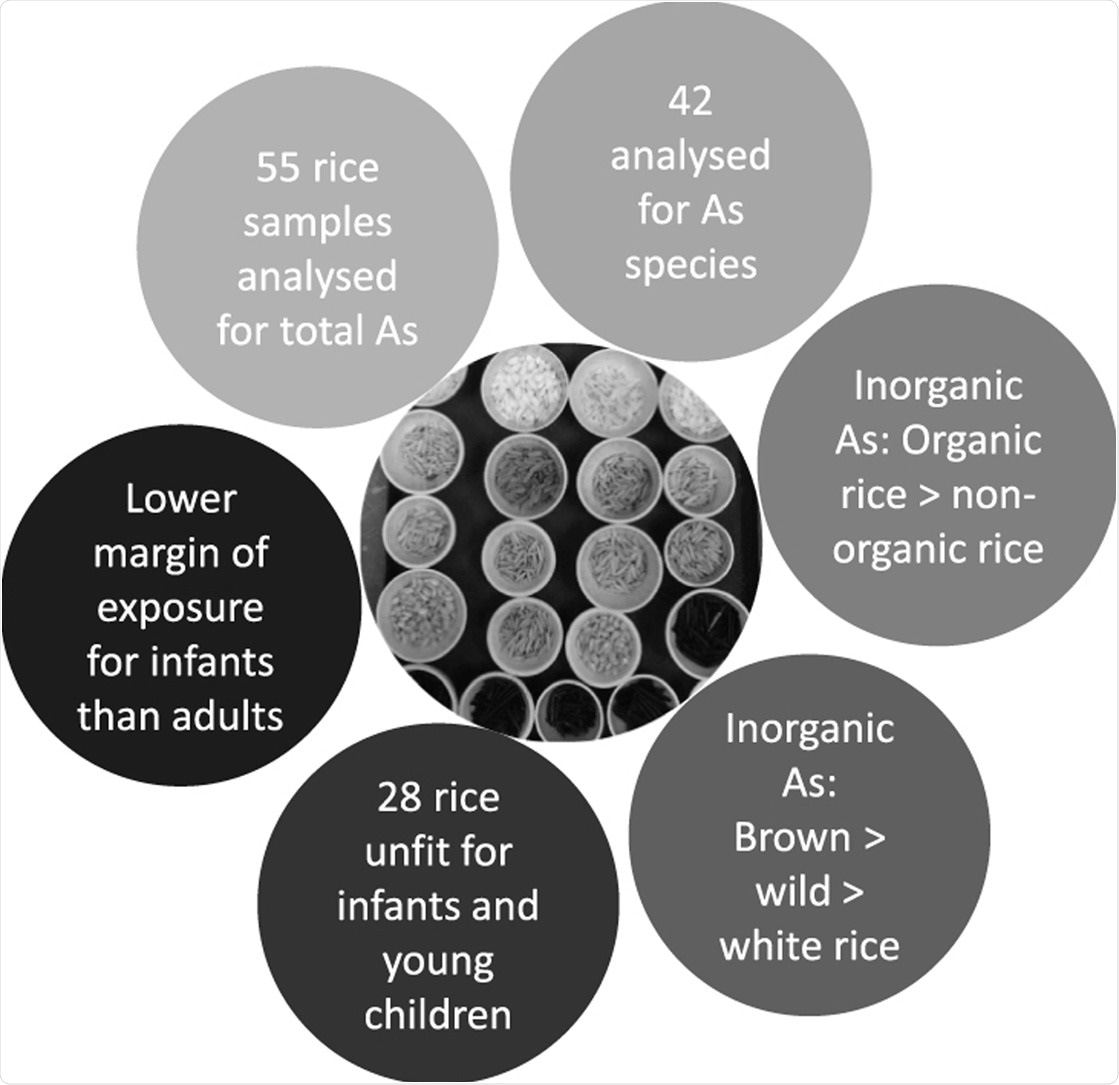
Image Credit: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651320304401
In a study published in the journal Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety (open access), a team at the University of Sheffield's Institute for Sustainable Food found 28 out of 55 rice samples sold in the UK contained levels of arsenic that exceeded European Commission regulations for rice meant for the consumption for infants or young children.
The research is the first to measure differences in human health risks from arsenic using a substantial number of rice varieties marketed in the UK.
The results showed that brown rice contained higher levels of the carcinogen than white or wild rice because it contains the bran, the outer layer of the grain. Meanwhile, organically grown rice was found to contain significantly higher levels than non-organically grown rice. White rice contained the lowest levels of arsenic.
Considering the health implications, the researchers concluded that babies under the age of one must be restricted to a maximum of 20g per day of the 28 rice varieties that breached regulations, in order to avoid risks of developing cancer in later life.
They have recommended that the UK government and European Commission introduce labeling to clarify whether rice is safe for consumption by babies and children under five.
Up to 90 percent of UK households buy rice, with the average person consuming around 100g per week. Rice and rice-based products are widely used for weaning and as baby food, due to their nutritional benefits and relatively low allergic potential, but, according to the European Food Safety Authority, children are two-three times more susceptible to arsenic risks than adults due to their lower body weight.
Arsenic, which is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, is water-soluble, so it accumulates in rice, which is grown in flooded fields more than other cereals. Arsenic exposure affects almost every organ in the body and can cause skin lesions, cancer, diabetes, and lung diseases.
Dr. Manoj Menon, Environmental Soil Scientist in the Department of Geography at the University of Sheffield and lead author of the study, said: "Brown and wild rice are healthy foods full of fiber and vitamins, and there is no need for grown-ups to avoid them, but it is concerning to see so many varieties sold in the UK breaching food safety regulations.
Rice products are often considered a safe option for babies and young children, but our research suggests that for more than half of the rice we sampled, infants should be limited to just 20g per day to avoid risks associated with arsenic. The government and the European Commission must introduce labeling to warn people of arsenic levels in rice to enable families to make informed food choices."
The research was funded as part of the UK's Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Food Network+.
The network brings together more than 750 international and multidisciplinary researchers from across the agri-food sector to work with experts from STFC's research facilities, all with the aim of solving some of the world's greatest food sustainability challenges.
Until April this year, the network was led by the University of Manchester. This is now being led by academics at the Institute for Sustainable Food.
The Institute for Sustainable Food at the University of Sheffield brings together multidisciplinary expertise and world-class research facilities to help achieve food security and protect the natural resources we all depend on.