China-based researchers have developed an improved technology that makes it slightly easier to understand cells. By using the Raman-Activated Cell Ejection and Sequencing (RACE-Seq) method, the researchers have successfully detected and sequenced individual cells from the environment to interpret the functions of the cells.
The procedure of Raman-Activated Cell Ejection and Sequencing (RACE-Seq). Image Credit: SU Xiaolu.
The researchers have recently published their study results in the Analytical Chemistry journal.
RACE-Seq is a useful technology to identify, isolate and sequence single-cells with particular function from environment, however, the success rate and quality of RACE-Seq has been quite low for environmental samples.”
SU Xiaolu, Study Author and Researcher, Single-Cell Center, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Scientists can understand the mechanistic associations between the genetic components and function of individual cells in nature, by using single-cell Raman sorting and sequencing tools, including RACE-Seq.
In the case of genetically varied settings, like soil found in the environment, the RACE-Seq technique helps to sort the cells depending on their functional roles—without impairing them. It also helps to sequence the cells’ genome to determine those mechanic connections between function and genetics.
In the RACE-Seq method, cells are placed onto a surface of a microchip and then air-dried instantly before irradiating them with a laser. Cells exhibiting the function being sorted for are detected and ejected into a receiving well on another chip. Then, the cells are ruptured and their genetic material is processed to find out the fundamental mechanical connection to the specific function of interest.
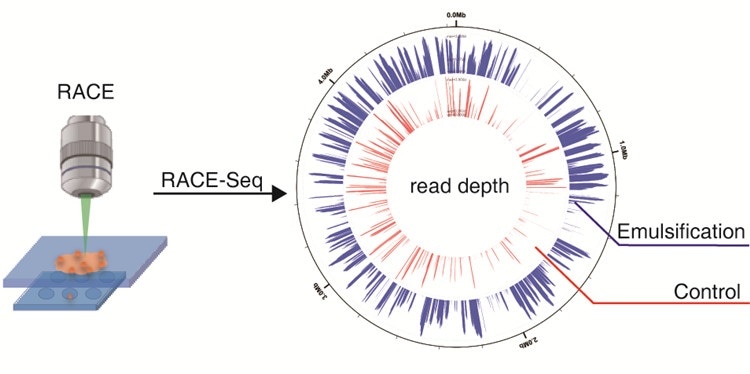
Earlier, this approach could produce around 20% coverage of genome for individual E. coli cells. The scientists have now enhanced the technique so that the genome coverage reaches about 50%.
Along with his research team, SU Xiaolu observed that adjusting the energy input of the laser allowed the cells to have a more improved output. The team also noted that the output was not improved by changing the temperature, duration, or other features of the other steps.
To deal with this issue, the scientists added oil before increasing the DNA of the sorted cells. This elegant yet simple operation minimizes the harmful impacts of Raman irradiation and significantly increases the completeness of the genomes.
In addition, this new protocol significantly enhances the experimental success rate of the RACE-Seq method, especially for soil microbiota, which are perchance the most complex microbial communities existing in nature.
Our findings provide a practical solution for enhancing RACE-Seq performance, and thus should make this technique more accessible to the many laboratories interested in single-cell sequencing around the globe.”
XU Jian, Director, Single-Cell Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The scientists also observed that the RACE-Seq technique is still incapable of producing good-quality genomes at accurately one-cell resolution from the environmental samples. The team is now exploring innovative technologies that can lead to the ultimate aim of functionally sorting and sequencing every microbial cell from natural settings.
Source:
Journal reference:
Su, X., et al. (2020) Rational Optimization of Raman-Activated Cell Ejection and Sequencing for Bacteria. Analytical Chemistry. doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05345.