Gene therapy offers an excellent potential for treating specific types of genetic defects and cancer, immunological diseases, infections, and wounds.
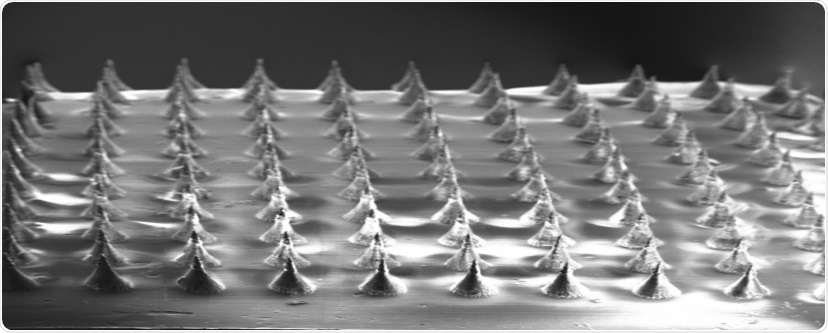
Microneedles for therapeutic gene delivery. Image Credit: Khademhosseini Laboratory.
These therapies work by transmitting genes into the patients’ cells, which subsequently generate therapeutic proteins to treat the disease.
When establishing the delivery method for these kinds of genes, there are benefits to selecting a local delivery instead of a systemic delivery of the genetic material. In the case of systemic delivery, unnecessary tissue accumulation or the genetic material can possibly become unstable.
Moreover, it is also beneficial to target the skin as a site for local delivery, because it can be easily accessed and contains lymph vessels, fluid, as well as immune cells on which the genetic material can work to begin treatment.
But in spite of these benefits, it is still hard to deliver genes within the skin. A perfect gene delivery method must have the ability to deliver the genetic material without producing toxicity or inflammation in the body and should also possess the ability to enter the skin layer effectively.
A collaborative research team, which also includes a group from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, has now published a method based on microneedles that fulfills these challenges. These microneedles are composed of a biocompatible material combined with nanoparticles that contain therapeutic genes.
This combination can be molded into a microneedle patch array to apply on the skin. Moreover, the microneedles are biodegradable, which means once they enter the skin, they will discharge the nanoparticles upon the degradation of microneedles.
In addition, the sustainability and timing of this release can be regulated by modifying the biomaterial preparation.
The researchers carried out elaborate tests to improve the discharge and performance of the gene-containing nanoparticles, and they also verified the efficacy of the genes.
This biodegradable microneedle patch with gene-delivering nanoparticles is an effective and minimally-invasive vehicle for local therapeutic gene delivery. This platform can be utilized for applications such as vaccinations, protein supplementation or gene editing.”
Wujin Sun, PhD, Study Author, Terasaki Institute Fellow
The development of such microneedles shows the potential for analogous gene delivery systems that can be modified according to the therapeutic genes selected.
This novel technology can offer a more effective method to treat skin and other types of cancers, diseases such as muscular dystrophy and psoriasis, and skin-related cosmetic needs. It can also be used as a technique for vaccine delivery against these diseases as breast or skin cancer, influenza, or COVID-19.
The ability to enable local therapeutic gene delivery using this microneedle system is a notable achievement. It opens the possibilities for a variety of clinical applications and synergizes with a number of platforms at the Terasaki Institute, which aims to leverage our ability to find personalized solutions for patients.”
Ali Khademhosseini, PhD, Study Senior Author, Director, and CEO, Terasaki Institute
Source:
Journal reference:
Qu, M., et al. (2020) Biodegradable microneedle patch for transdermal gene delivery†. Royal Society of Chemistry. doi.org/10.1039/D0NR02759F.