A recent study has illuminated the significance of the protein STAP-1 in activating specific immune cells. Comprehending the role of STAP-1 in these cells could offer researchers valuable insights into immune-related disorders and potential therapeutic approaches.
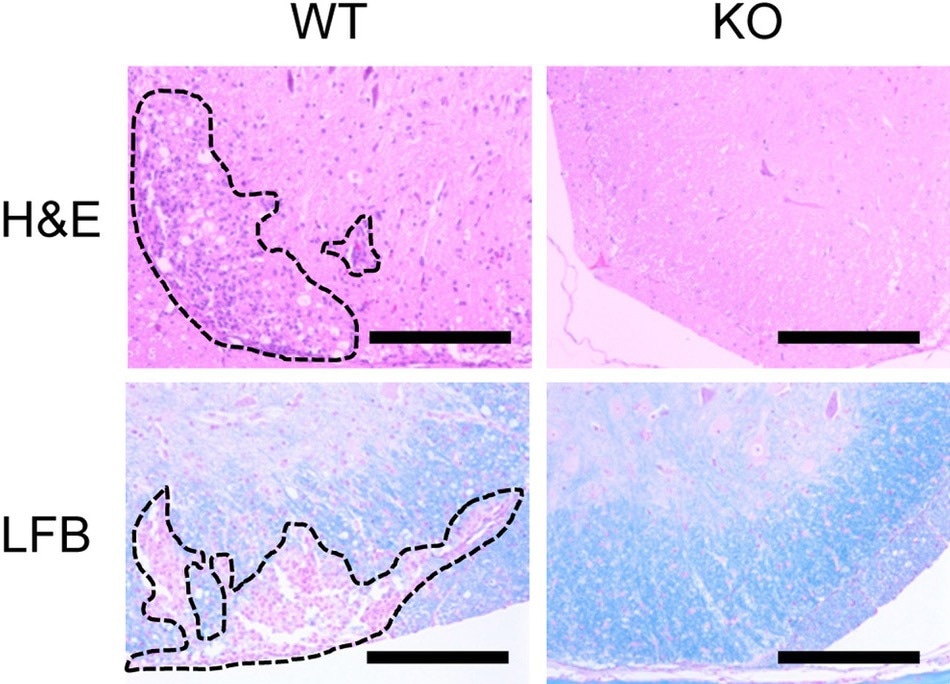 The inflammatory reaction in the spinal cords of STAP-1 knockout (KO) mice was less severe than that of wild-type (WT) mice (top panels). In parallel, the spinal cords of STAP-1 KO mice exhibited less demyelination - loss of the myelin sheath that surrounds nerves - when compared with those of WT mice (bottom panels). Image Credit: Kota Kagohashi, et al. The Journal of Immunology
The inflammatory reaction in the spinal cords of STAP-1 knockout (KO) mice was less severe than that of wild-type (WT) mice (top panels). In parallel, the spinal cords of STAP-1 KO mice exhibited less demyelination - loss of the myelin sheath that surrounds nerves - when compared with those of WT mice (bottom panels). Image Credit: Kota Kagohashi, et al. The Journal of Immunology
The study revealed that STAP-1 plays a crucial role in activating T cells, which are vital white blood cells responsible for defending the body against infections and preserving overall health. T cells excel at identifying foreign molecules, known as antigens, that prompt an immune response, and orchestrate specific reactions to eradicate pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
The Journal of Immunology recently published the study that examined the impact of STAP-1 on immune response. The study found that STAP-1 functions as a mediator, aiding communication between various proteins within cells and enabling signals to be transmitted from one molecule to another.
Our findings provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying T cell activation and the development of immune disorders. We found that STAP-1 plays an important role in regulating immune responses, particularly in the activation and functioning of T cells.”
Tadashi Matsuda, Professor and Study Lead Author, Hokkaido University
To start an immune response, T cells require two signals. Firstly, they recognize antigens presented by other cells, also known as antigen-presenting cells, using their T cell receptor. Secondly, the T cells need co-stimulatory signals provided by molecules on the antigen-presenting cells to become fully activated and initiate the immune response.
The study revealed that STAP-1 aids T cells in communicating and responding to signals, particularly those initiated by the T cell receptor. T cells lacking STAP-1 experienced difficulties in properly receiving and transmitting signals, leading to decreased production of specific immune molecules known as cytokines.
This reduction in cytokine production can contribute to inflammation or autoimmune diseases, where the immune system erroneously targets healthy tissues and organs.
The team discovered that STAP-1 interacts with other proteins implicated in T-cell signaling, creating a complex network that contributes to regulating T-cell activity.
Their observations indicated that cells lacking STAP-1 exhibited reduced inflammation in disease models such as multiple sclerosis and asthma. This suggests that STAP-1 may play a role in the pathogenesis of these conditions.
These findings mark a significant advancement in comprehending immune system regulation. Subsequent research endeavors can expand upon this groundwork by investigating the therapeutic potential of STAP-1 for addressing immune-related disorders.
Source:
Journal reference:
Kagohashi, K., et al. (2024) Role of Signal-Transducing Adaptor Protein-1 for T Cell Activation and Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Demyelination and Airway Inflammation. The Journal of Immunology. doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2300202.